Lowess Smoothing
About Lowess Smoothing
Use Lowess models to fit smooth surfaces to your data. The names “lowess” and “loess” are derived from the term “locally weighted scatter plot smooth,” as both methods use locally weighted linear regression to smooth data. The process is weighted because the toolbox defines a regression weight function for the data points contained within the span. In addition to the regression weight function, the Robust option is a weight function that can make the process resistant to outliers.
For more information on these two types of smoothing fit, see Local Regression Smoothing.
Selecting a Lowess Fit Interactively
In the Curve Fitting app, select Lowess from
the model type list.
You can use the Lowess model type
to fit smooth surfaces to your data with either lowess or loess methods.
The Lowess fits use locally weighted linear
regression to smooth data.
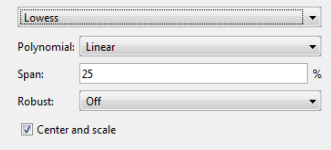
You can specify the following options:
Select
LinearorQuadraticfrom the list to specify the type of Polynomial model to use in the regression. In Curve Fitting Toolbox™,lowessfitting uses a linear polynomial, whileloessfitting uses a quadratic polynomial.Use Span to specify the span as a percentage of the total number of data points in the data set. The toolbox uses neighboring data points defined within the span to determine each smoothed value. This role of neighboring points is the reason why the smoothing process is called “local.”
Tip
Increase the span to make the surface smoother. Reduce the span to make the surface follow the data more closely.
The Robust linear least-squares fitting method you want to use (
Off,LAR, orBisquare). The local regression uses the Robust option. Using the Robust weight function can make the process resistant to outliers. For details, seeRobuston thefitoptionsreference page.
Tip
If your input variables have very different scales, turn the Center and scale option on and off to see the difference in the surface fit. Normalizing the inputs can strongly influence the results of a Lowess fitting.
For an interactive example using Lowess, see Surface Fitting to Franke Data.
Fit Lowess Models Using the fit Function
This example shows how to use the fit function to fit a Lowess model to data.
Load some data and fit a Lowess model by specifying 'lowess' when calling the fit function.
load franke f = fit([x y],z,'lowess')
Locally weighted smoothing linear regression:
f(x,y) = lowess (linear) smoothing regression computed from p
Coefficients:
p = coefficient structure
plot(f,[x y],z)

For a command-line example using Lowess, see Fit Smooth Surfaces To Investigate Fuel Efficiency.